research

(Professor Hyunjoo Lee (left) and Ph.D. candidate Jiwhan Kim)
A research team co-led by Professor Hyunjoo Lee at the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST and Professor Jeong Woo Han from the University of Seoul synthesized highly stable high-Pt-content single atom catalysts for direct formic acid fuel cells. The amount of platinum can be reduced to 1/10 of that of conventional platinum nanoparticle catalysts.
Platinum (Pt) catalysts have been used in various catalytic reactions due to their high activity and stability. However, because Pt is rare and expensive, it is important to reduce the amount of Pt used. Pt single atom catalysts can reduce the size of the Pt particles to the size of an atom. Thus, the cost of Pt catalysts can be minimized because all of the Pt atoms can participate in the catalytic reactions. Additionally, single atom catalysts have no ensemble site in which two or more atoms are attached, and thus, the reaction selectivity is different from that of nanoparticle catalysts.
Despite these advantages, single atom catalysts are easily aggregated and less stable due to their low coordination number and high surface free energy. It is difficult to develop a single atom catalyst with high content and high stability, and thus, its application in practical devices is limited.
Direct formic acid fuel cells can be an energy source for next-generation portable devices because liquid formic acid as a fuel is safer and easier to store and transport than high-pressure hydrogen gas.
To improve the stability of Pt single atom catalysts, Professor Lee’s group developed a Pt-Sn single atom alloy structure on an antimony-doped tin oxide (ATO) support. This structure has been proven by computational calculations which show that Pt single atoms substitute antimony sites in the antimony-tin alloy structure and are thermodynamically stable. This catalyst has been shown to have a higher activity up to 50 times per weight of Pt than that of the commercial catalyst, Pt/C, in the oxidation of formic acid, and the stability of the catalyst was also remarkably high.
Professor Lee’s group also used a single atomic catalyst in a 'direct formic acid fuel cell’ consisting of membranes and electrodes. It is the first attempt to apply a single atomic catalyst to a full cell. In this case, an output similar to that of the commercial catalyst could be obtained by using 1/10 of the platinum compared to the commercial Pt/C catalyst.
Ph.D. candidate Jiwhan Kim from KAIST was the first author of the research. This research was published online on September 11 in Advanced Energy Materials.
This research was carried out with the support of the Samsung Electronics Future Technology Development Center.
(Figure 1. Concept photograph for Pt single atom catalysts.)
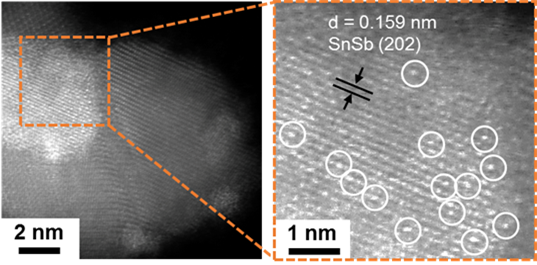
(Figure 2. Pt single atom catalysts by HAADF-STEM analysis (bright white circles))
-
research Novel Material Properties of Hybrid Perovskite Nanostructures for Next-generation Non-linear Electronic Devices
(from left: Juho Lee, Dr. Muhammad Ejaz Khan and Professor Yong-Hoon Kim) A KAIST research team reported a novel non-linear device with the founding property coming from perovskite nanowires. They showed that hybrid perovskite-derived, inorganic-framework nanowires can acquire semi-metallicity, and proposed negative differential resistance (NDR) devices with excellent NDR characteristics that resulted from a novel quantum-hybridization NDR mechanism, implying the potential of perovskite nano
2019-02-22 -
research Hierarchical Porous Titanium Nitride Synthesized by Multiscale Phase Separation for LSBs
(from left: Professor Jinwoo Lee and PhD candidate Won-Gwang Lim) A KAIST research team developed ultra-stable, high-rate lithium-sulfur batteries (LSBs) by using hierarchical porous titanium nitride as a sulfur host, and achieved superior cycle stability and high rate performance for LSBs. The control of large amounts of energy is required for use in an electric vehicle or smart grid system. In this sense, the development of next-generation secondary batteries is in high
2019-01-28 -
research Highly Scalable Process to Obtain Stable 2D Nanosheet Dispersion
(Professor Do Hyun Kim and his team) A KAIST team developed technology that allows the mass production of two-dimensional (2D) nanomaterial dispersion by utilizing the characteristic shearing force of hydraulic power. The 2D nanosheet dispersion can be directly applied to solution-based processes to manufacture devices for electronics as well as energy storage and conversion. It is expected to be used in these devices with improved performance. There have been numero
2018-12-19 -
research Characteristics of Submesoscale Geophysical Turbulence Reported
A KAIST research team has reported some of unique characteristics and driving forces behind submesoscale geophysical turbulence. Using big data analysis on ocean surface currents and chlorophyll concentrations observed using coastal radars and satellites has brought better understanding of oceanic processes in space and time scales of O(1) kilometer and O(1) hour. The outcomes of this work will lead to improved tracking of water-borne materials and performance in global and regional climate
2018-12-13 -
research Silk Adhesive Paves the Way for Epidermal Electronics
(from left: Dr. Ji-Won Seo, Professor Hyunjoo Jenny Lee and PhD candidate, Hyojung Kim) Producing effective epidermal electronics requires a strong, biocompatible interface between a biological surface and a sensor. Here, a KAIST team employed a calcium-modified silk fibroin as a biocompatible and strong adhesive. This technology led to the development of epidermal electronics with strong adhesion for patients who need drug injections and physiological monitoring over a long
2018-11-21